Medical experts associate some of the pains that we generally go through, with some serious conditions that warrant immediate medical attention. Pain is a natural reaction – a response of the body to some inherent problem inside it. Although none of us like it, the pains, in fact, are natural signals that tell us that something is amiss inside our body.
We generally ignore the little pains in the shoulders and wrists that we get after moving the furniture in the living room. They usually go away after a couple of days and we know they are not serious. Over the years, we are also tuned to live with the pains. Due to work pressure and the seemingly other important preoccupations in life, we take them for granted.
But, unfortunately, not giving proper attention to those apparently innocuous pains may have serious consequences and sometimes prove to be fatal. So, how do you know which of these pains may be ominous – a guiding symptom to something gravely wrong inside the body?
Our consultation with doctors in medicine, psychiatric, geriatrics and cardiology revealed that the following pains should be given immediate medical attention:
7 – An excruciating headache

Sandra Fryhofer, MD, MACP and spokeswoman for the American college of Physician said, “Although your cold and headache could be due to a sinus problem, it may also be due to a brain tumor or brain hemorrhage. So, get it investigated till you are sure of the reason.”
Sharon Brangman, MD, FACP, spokeswoman for the American Geriatric Society also agrees with this and says that when people complain of a severe headache they ever had in their lives, invariably it turns out to be a typical case of a brain aneurysm. So, seek immediate emergency check-up.
6 – Pain and feeling of heaviness in the jaw, throat, shoulders, chest and abdomen

Discomfort and pain in the chest may sometimes be due to cardiac ailments. Jerome Cohen, MD, Cardiologist says that cardiac patients complain of a feeling of heaviness on the chest. They feel as if the chest is pressurized by some heavy weight.
People with heart problem also have discomfort and pain in the throat, jaws, left arm, shoulder, upper chest and abdomen. At times, there might also be nausea. Cohen says in this regard, “If the pain and discomfort is persistent and without any reason, then one should immediately call 911 or consult a physician and get emergency care, irrespective of the age of the patient. Many times, people wrongly take these symptoms to be cases of heartburn or GI distress. If the investigation proves that they are not associated with any cardiac ailment, then it is okay. But do take precaution.”
He also opines that the intermittent discomforts that occur during emotional disturbance, excitement and physical exertion should also be investigated. If you have it after going on a walk and such discomforts gets worse during hot and cold weathers, then it could be angina.
According to Cohen, who happens to be the director of preventive cardiology at Saint Louis University School of Medicine, more women succumb to it more than men, although women are at lower risks of heart disease than men at any age and their signs of discomforts are also less obvious. Often, a symptom like GI distress, bloating, discomforts in abdomen and exhaustion are misinterpreted and due medical attention is not given. There is also a greater risk of cardiac ailments after menopause among women. Hence, women as well physicians should take note of such symptoms.
5 – Pain between the shoulders and lower back

Even though such pains are mostly due to arthritis, cardiac attack or problems in the abdomen could also be the underlying reasons. The pain can be due to aortic dissection that manifests as a sudden or nagging pain. People with a history of hypertension, diabetes, smoking habit and cardiovascular problems are at high risk.
4 – Excruciating pain in the abdomen
It can be due to appendicitis and should be immediately operated, lest it would rupture. Other serious problems associated with pain in the abdomen region, could be stomach ulcers, intestinal blockage and problems in gall bladder or pancreas and hence should be investigated thoroughly.
3 – Pain in the calf

Almost two million Americans suffer from deep vein thrombosis (DVT), which may result in pain in the calf.
“People suffering from it develop blood clots in the deep veins of the legs, which may cause a pulmonary embolism (a clot in the lungs). It can be life-threatening,” says Fryhofer. According to Brangman, who is professor and chief of geriatrics at SUNY Upstate Medical University in Syracuse, N.Y., there can only be swelling without any pain, and medical advice should be sought even in such condition.
Cancer, pregnancy, obesity, immobility are some of the associated conditions of deep vein thrombosis.
2 – Burning sensation in the feet or legs
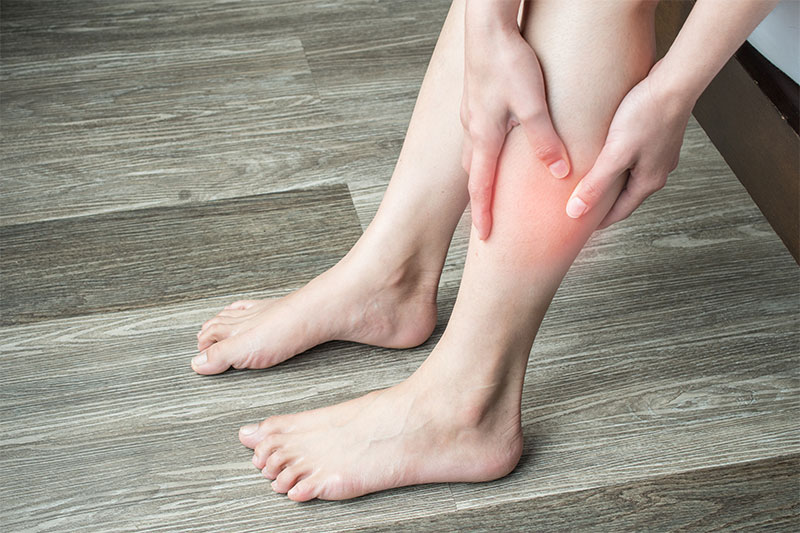
Brangman says that the sensation burning or the pricking of needle in the feet or legs is the indicator of nerve damage and diabetes. The American Diabetes Association estimates that 25 percent of the 24 millions of Americans with diabetes are undiagnosed. So, people, who are yet to be diagnosed with diabetes, should be alert of such symptoms.
1 – Indeterminate, undefined and medically unexplained pain

“Persons suffering from depression complain of many vague and unexplained pains. They may be abdominal pain, headache or pains in different body parts,” explains Thomas Wise, MD, psychiatrist and chairman of the psychiatric department at Inova Fairfax Hospital in Fairfax, Va.
“Since the pain is not very often severe, it is ignored by those people suffering from it and also by their family members and physicians. Moreover, the people suffering from depression are unable to express their feelings properly,” Wise adds.
There should also be other associated symptoms of depression in order to fully diagnose a case of depression.
“But people, who find it difficult getting along with others, lose interest in going through their daily chores or are unable to think and express articulately should seek medical advice immediately, as timely treatment can avert any structural damage to the brain,” Wise cautions.


